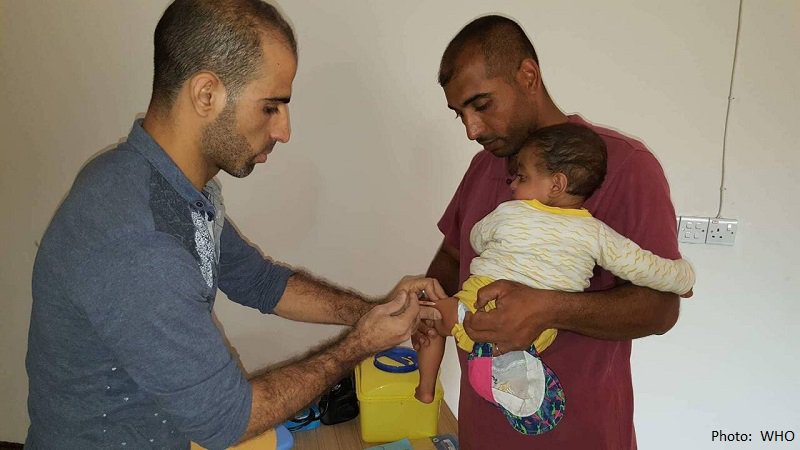
The World Health Organization (WHO) welcomes a new contribution of US$24 million from the US Agency for International Development’s Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance (USAID-OFDA) to strengthen primary, secondary and preventive health services in conflict-affected governorates in Iraq.
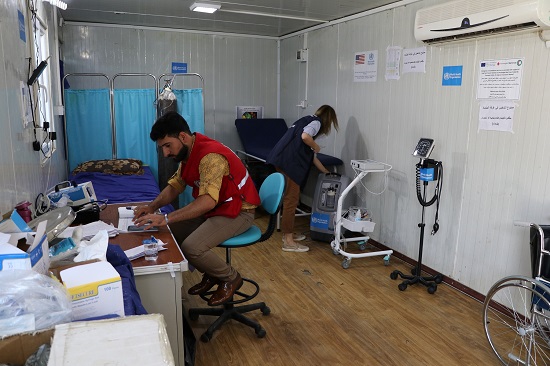
Access to improved life-saving health services will be ensured for approximately 3.5 million beneficiaries in seven governorates where health systems have been weakened by years of conflict.
“WHO is grateful to USAID-OFDA for its continued support, which enables us to maintain the delivery of uninterrupted quality health care services to millions of highly vulnerable women, children and the elderly living in severely affected areas,” said Dr. Adham Ismail Abdel Moniem, WHO Representative in Iraq.
As of October 2019, more than 4.3 million people have returned to their homes of origin, while approximately 1.5 million remain displaced in camps, informal settlements, and host communities across Iraq.
Through this new contribution from USAID-OFDA, WHO will scale up its support to national health authorities and partners to find sustainable solutions for the treatment of common diseases and environmental health emergencies. In parallel, WHO will establish primary health care centers in camps hosting displaced people, and rehabilitate primary health care facilities in areas of return.
The contribution will also cover the provision of prosthetics and physical rehabilitation for amputees, in addition to supporting mental health care services for those in need. Clinical management of rape and Gender-Based-Violence survivors is also among WHO’s priorities for 2019/20.
WHO has received considerable support from USAID/OFDA which was vital in supporting the health emergency response throughout the crisis in Iraq. During the Mosul conflict in 2014, mobile clinics were deployed, field hospitals were established close to the frontlines, and medicines and medical supplies were provided to health facilities delivering emergency health services in Dohuk, Ninewa, Anbar, and Kirkuk.
Medical waste management services were also supported, and a total of 76,000 kgs of medical waste was collected, sorted and disposed to prevent risk of cross-contamination.
“WHO has been able to maintain its work in Iraq through the commitment, cooperation, and generous contributions of donors such as the US Agency for International Development’s Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance,” said Dr. Abdel Moniem.
(Source: UN)